Written by Tinka Harvard

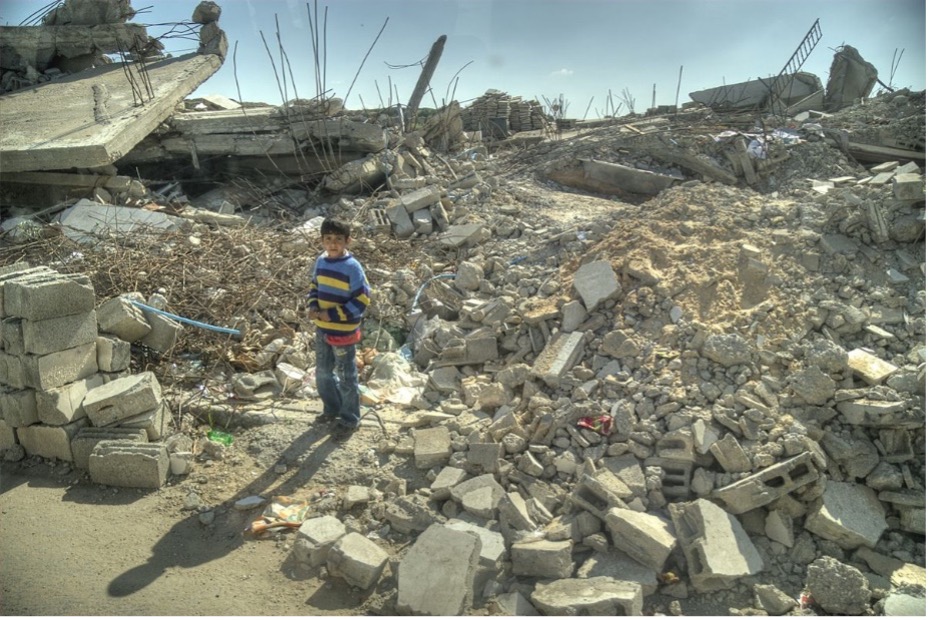
A worker at a construction site along Israel’s 150-mile long fence on the Egyptian Sinai border was completed in 2013. (Photo credit: Ahmad Gharabli)[I]
Hourglass (a literal translation of the Hebrew ‘שְׁעוֹן הַחוֹל,’ or ‘sand clock’) is the name of the project that refers to a fence built by Israel along its border with Egypt to decrease the influx of asylum seekers from Sudan and Darfur.[i] Migrants are often individuals and communities fleeing conflict and fragility in their home countries and seeking refuge and safety from violence or economic poverty.[ii]
Fragility and conflict create a continuum of reasons people leave their country of origin, voluntarily or involuntarily, including national or international war, unstable government, environmental disasters, economic instability, and terror.[iii] Fragile states contributed 18 million migrants and 8 million refugees in 2000.[iv] By mid-2020, the global refugee population had reached 26.3 million.[v]
When people are able to migrate, where do they go?
About half of the world’s migrants travel to high-income countries that are members of the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD). Seeking refuge in Israel provides safety from extreme violence and an opportunity for economic betterment. It can also be a bridge to eventually entering Europe, which provides even more prospects for safety and freedom from poverty.[vi]
What is the conflict and fragility about
for migrants travelling to Israel?
Migrants and refugees from Sudan, in particular, migrate or flee because of government destabilization and economic collapse, which are results of the on-and-off civil wars since 1955. This has forced millions of Sudanese to leave the country, often crossing into Israel by land via Egypt to seek asylum. They are forcibly displaced by war and other factors, including the civil war between the predominantly Muslim north and the rebels from the south, where people are mostly Christian or follow traditional African religions.[vii]
Since social exclusion is a process that ‘at any one time, people are situated on a multidimensional continuum,’ being excluded socially in one instance often creates a disconnect in many other ways. That exclusion then expands for both individuals as well as groups and communities.[viii]
Religion can bring people together, but, ironically, it is often used to keep them separated. This separation by religion—or positioning of one religion over another—has been used by Western cultures to gain control of people.[ix] To aid in this control, Western Christianity was not eliminated but rather absorbed by the state, reducing ecclesiastical power, all while creating a myth that the Western religion of Christianity was a ‘better’ religion. This meant that ‘non-Western’ religions were ‘othered’ and deemed inferior. This created a separation of people as well, not only in faith traditions, which translated to non-Western people being considered ‘violent, subrational, sub modern,’ and even sexist.[x]
How do we begin to eliminate the borders between us?
As myths have been propagated about Western Christianity being superior to other religions—which demonized, othered, and divided people and nations—it begs the question: What existed before the myths that one religion or group of people was better than the other religions or groups? What existed before borders were created? What existed before the West created its own separations? Guidance from Elie Wiesel, writing in The Gates of the Forest, may lend a helping hand in pointing toward answers to these questions. In this novel, he writes about the importance of telling our stories when we are trying to find our way back together again, sans separation and borders between each of us:
Then it fell to Rabbi Israel of Rizhyn
To overcome misfortune.
Sitting in his armchair, his head in his hands,
He spoke to God: ‘I am unable to light the fire
And I do not know the prayer;
I cannot even find the place in the forest.
All I can do is to tell the story,
And this must be sufficient.’
And it was sufficient.[xi]
Theologian John Swinton wants to foster inclusion and eliminate social exclusion and its devastating consequences. In a podcast interview of Swinton by host Sarah Kife, he calls for lifting the voices that have been repressed and stigmatized as we flesh out ways for us all to be fully human in the marvel of diversity.[xii]
Swinton encourages us all to be present and to listen to one another on this journey of being fully human. As the host, Kife reminds us, ‘we need each other to remember who we are, especially in times of crises, and how to find one’s voice in a world that can stigmatize and oppress people simply for being “different.”’[xiii] Swinton’s and Kife’s ideas go a long way toward the inclusion of ‘the stranger’ and help to counter Israel’s current stance of classifying non-Jewish asylum seekers as ‘infiltrators, posing a danger to the Jewish character of Israel.’[xiv]
There Is Hope for the Future and an Invitation to Get Involved
‘Closed borders are one of the world’s greatest moral failings, but the opening of borders is the world’s greatest economic opportunity.’
—Alex Tabarrok[xv]
There are several ways to assist in decreasing social exclusion with the hope of eliminating it. One argument for open borders is that it is economically beneficial because new immigrants often either possess talent and skills sought after by the host country or are willing to take on work that citizens are no longer interested in doing. Open borders are also morally just since freedom of movement is a fundamental human right.[xvi] Existing efforts to help migrants and asylum seekers in different parts of the world range from a mission of love to direct action. For example, Border Angels, an organization whose motto is ‘love has no borders,’ promotes a culture of love in their activism to defend the rights of migrants and refugees.[xvii] Also, activists in Poland have used brute force to remove a barbed-wire border fence constructed by the Polish government to prevent migrants from crossing into Poland from Belarus.[xviii]
There are many ways to get involved and make a difference. Support of existing organizations and movements is one way, and many are active on social media and can be found with careful research. But new ideas to help in the efforts toward decreasing marginalization and social exclusion are needed. No act of help goes wasted. It can all be used for the good. Begin where you are.
References
[I]. Noga Tarnopolsky. ‘Israel Built a New Border Wall to Prevent Migrants from “Smuggling in Terror,”’ TheWorld, December 5, 2013. https://theworld.org/stories/2013-12-05/israel-built-new-border-wall-prevent-migrants-smuggling-terror.
[i]. Bina Engineering&Management Ltd. ‘Israel-Egypt Barrier Project,’ 2016. https://www.binagroup.co.il/israel-egypt-barrier-project.
[ii]. ‘Sudan-Israel Deal Fuels Migrants’ Fears,’ BBC News, 21 December 2020. https://www.bbc.com/news/world-africa-55333131.
[iii]. Anke Hoeffler. ‘Out of the Frying Pan into the Fire? Migration from Fragile States to Fragile States.’ OECD Development Co-operation Working Papers, No. 9. Paris: OECD Publishing, 2013, p. 6. https://doi.org/10.1787/5k49dffmjpmv-en.
[iv]. Ibid, p. 4.
[v]. OECD, ILO, IOM, and UNHCR. 2020 Annual International Migration and Forced Displacement Trends and Policies Report to the G20. Paris: OECD Publishing, 2020. https://www.oecd.org/els/mig/FINAL-2020-OECD-ILO-UNHCR-IOM-G20-report.pdf.
[vi]. Hoeffler, p. 8.
[vii]. ‘Facts & Stats,’ Frontline World, undated. https://www.pbs.org/frontlineworld/stories/sudan/facts.html.
[viii]. Hilary Silver. ‘The Process of Social Exclusion: The Dynamics of an Evolving Concept.’ London: Chronic Poverty Research Center, 1 October 2007, p. i. https://ssrn.com/abstract=1087789 or http://dx.doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.1087789.
[ix]. William T. Cavanaugh. ‘The Invention of Fanaticism,’ in Faith, Rationality and the Passions, by Sarah Coakley. Hoboken, NJ: Wiley Publishing, 2012, p. 33.
[x]. Ibid, p. 29.
[xi]. Elie Wiesel. The Gates of the Forest. New York: Schocken Books, 1996.
[xii]. ‘Sanctuary: Mental Health Ministries.’ Sarah Kift podcast, episode 1, with John Swinton, 30 January 2020. https://www.sanctuarymentalhealth.org/2020/01/29/john-swinton/.
[xiii]. Ibid.
[xiv]. Dina Kraft and Sara Miller Llana. ‘Denied Asylum in Israel, Eritreans Are Welcomed by Canadian Jews.’ The Christian Science Monitor, 21 January 2022. https://www.csmonitor.com/World/2022/0121/Denied-asylum-in-Israel-Eritreans-are-welcomed-by-Canadian-Jews.
[xv]. Alex Tabarrok. ‘The Case for Getting Rid of Borders—Completely,’ The Atlantic, 10 October 2015. https://www.theatlantic.com/business/archive/2015/10/get-rid-borders-completely/409501/.
[xvi]. Ibid.
[xvii]. Border Angels website. https://www.borderangels.org/.
[xviii]. Daniel Tilles. ‘Activists Detained in Poland for Trying to Remove Fence on Belarus Border Amid Migrant Surge,’ Notes from Poland, 30 August 2021. https://notesfrompoland.com/2021/08/30/activists-detained-in-poland-for-trying-to-remove-fence-on-belarus-border-amid-migrant-surge/.